Description
Chatbot Lessons for Ages 13-18
Chatbot lessons for students can be fun to teach. In TechnoChatbot AI, students become chatbot developers. They use both Scratch coding and a free bot-builder to design chatbots that improve the lives of others. To start they explore the practical applications of this AI technology and how it eliminates mundane, repetitive tasks. Once familiar with the possibilities of natural language processing, they design their own bots. First, they build a simple rule-based chatbot for an event that can answer attendees’ questions using keyword matching. Next, they code a transactional chatbot that can do one job, which is take a customer order for a school fundraiser. Finally, they train a conversational chatbot to act as a virtual agent for an organization. It will answer questions, give directions, provide contact details, and more. Optional challenges explore the history of chatbots, large language models such as Chat GPT, and chatbot analytics.
Become Chatbot Developers
Transform students into chatbot developers. They build virtual assistants that can eliminate boring, repetitive tasks. Step-by-step instructions explain how to create chatbots that can assist event attendees, record order details for a school fundraiser, or answer new members questions about a local organization.
Artificial Intelligence Course for Teens
Lessons encourage students to consider the practical applications of AI, as well as its strengths and limitations. Activities connect to student’s daily lives such as attending school dances, raising money for a team or band, or ordering food at the cafeteria.
Hands-on Learning Explores AI Careers
In TechnoChatbot AI, students explore how chatbots can help businesses become more efficient while improving customer relationships. Throughout the activities a strong emphasis is placed on recognizing the needs of the end-user. This is a meaningful way to investigate professions that use natural language processing.
Flexible Assignments are Ideal for Middle or High School
Students can build rule-based, transactional, or conversational chatbots. Build one bot – or all three. Tasks increase in complexity. The project begins with keyword matching and dialog flow and then extends to default responses, training techniques, and more.
Think Like a Chatbot Developer
Assignments have students apply computational thinking to predict user questions, build response lists, and direct the flow of a conversation. Planning sheets help students invent their chatbots. Samples offer a source of inspiration. As well, design tips and challenges promote creativity and originality in their bots.
The TechnoChatbot AI course has 20 assignments divided into six sessions.
Session 1: Introduction to Chatbots
Students explore the practical applications of chatbots. They interact with chatbots to recognize how they communicate with humans. This exploration includes a critical examination of their strengths and limitations. Later, they prepare to create their own chatbots by registering for a Scratch account. This will be used in upcoming Sessions to build an event and order chatbot. To extend learning, an optional activity provides insight into key historical moments in chatbot development.
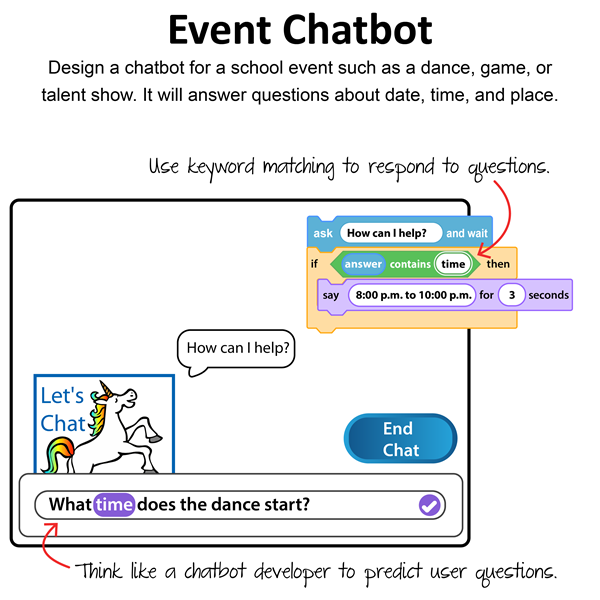
Session 2: Design an Event Chatbot
Students build a chatbot for an upcoming school event using Scratch coding. It could be a prom, school dance, spirit day, talent show, or retirement party. The chatbot will answer attendees' questions. To make the bot appear intelligent, it uses if-then logic and keyword matching. Upon completion, students evaluate their chatbots' limitations. An optional activity about artificial intelligence will expand students' knowledge of large language models.
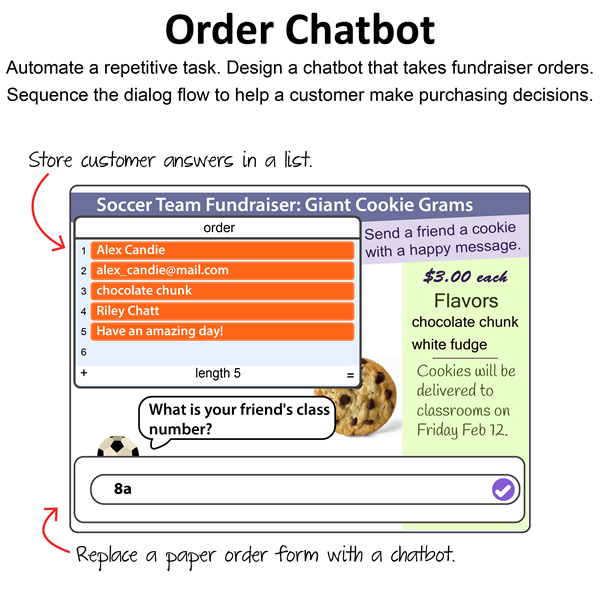
Session 3: Create an Order Chatbot
Students create an order chatbot using Scratch coding. It is a transactional chatbot, which can do one action. It will simplify the task of taking school fundraiser orders for items such as hats, cookies, or flowers. Just like a real salesperson, the bot will ask questions to help the customer make purchasing decisions. It will store their answers in a list. At the end of the conversation, the customer will be able to edit and then submit their order. This task expands students' knowledge of the practical applications of chatbots. In addition, it also introduces the use of lists, if-else logic, and broadcasting. An optional activity for using a chatbot to create a support ticket will develop a deeper understanding of how this technology can be used to automate tasks.
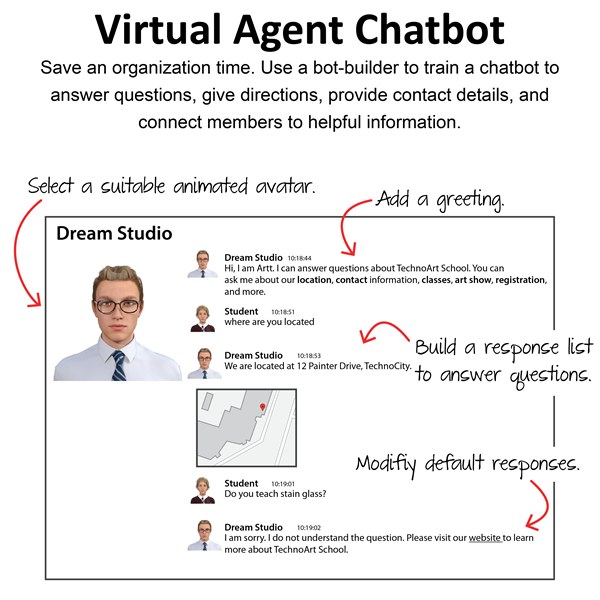
Session 4: Design a Virtual Agent
Students use the bot-builder app, Bot Libre, to design a virtual agent for a school or an organization. It will provide help to a new student or member. The chatbot will use natural language processing to answer common questions, provide directions, connect a user to information sources, and more. To start, they select a topic such as a local drama club, sports team, or art class. Next, they create a bot and then chat with it to discover what it does and does not know. Afterwards, they select an animated avatar and voice that will appeal to users. An extension activity emphasizes the need to be a responsible digital citizen by examining the Bot Libre terms of use and privacy policy.
Session 5: Train the Virtual Agent
Students train their virtual agent to increase its intelligence. To start, they view pre-programmed responses to verify the chatbot's existing knowledge base. Next, they add a new greeting and modify default responses to make the bot friendly and helpful. The training continues by adding questions and answers for common requests such as directions and contact information. Students then share their chatbot with a friend to test the design. They analyze the conversation to improve responses. An extension activity explains how to import data into the chatbot to increase its ability to correctly reply to users.
Session 6: Deploy the Virtual Agent
Students deploy their virtual agent. To prepare they use a checklist to verify that the chatbot can complete essential tasks. Once they are certain it is ready to use, they share their bot. This allows new members or students to get the information they need about an organization.
Optional Chatbot and Artificial Intelligence Lessons
- History of Chatbots: Recognize importance of events.
- AI Chatbots and You: Critically think about LLM.
- Import a Response List: Use a spreadsheet to add questions and answers.
Think Like a Chatbot Developer | Explore Artificial Intelligence Careers
In TechnoChatbot AI, students become chatbot developers. They build chatbots using Scratch coding and the free bot-builder, Bot Libre. Each task requires students to apply computational thinking to design a bot that can mimic the flow of a real conversation. The activities are designed to provide an understanding of the practical applications of chatbots. Moreover, this project is a fun exploration of the power of artificial intelligence and natural language processing.
- Recognize technologies that make a chatbot seem intelligent
- Describe the practical applications of chatbots
- Evaluate the strengths and limitations of chatbots
- Demonstrate an awareness of chatbot users' needs
- Plan and organize chatbots that will perform specific tasks
- Identify ways to give a chatbot personality
- Predict user questions and how they will phrase input
- Train a chatbot to respond accurately to users
- Test a chatbot and refine the design
- Deploy a chatbot for others to use
Chatbot Lessons for Students, Artificial Intelligence | TechnoChatbot AI
DownloadBecome chatbot developers. Improve the lives of others. Build an event chatbot, order chatbot, and virtual agent.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.